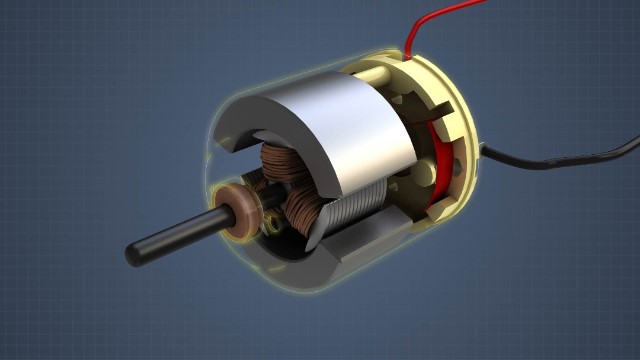
DC Motor Types
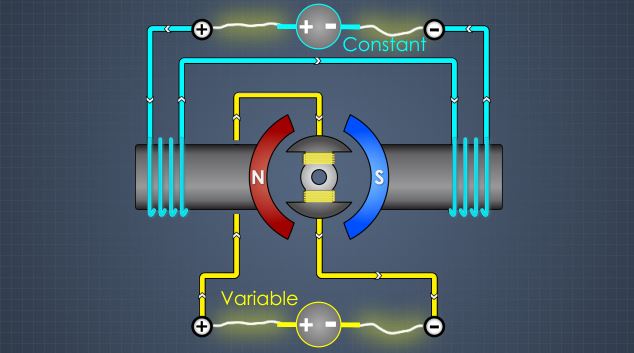
DC motors are electrical motors powered by direct current, or DC. DC is a type of electrical current that flows in one direction only, from sources such as batteries or solar panels. DC may also be produced through the use of a rectifier, which is an electrical device which converts alternating current (AC) to DC. This module will describe the design, operation, and applications of series, shunt, compound, permanent magnet, and separately excited motors.





Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.
Course Details
Learning Objectives
• Describe the design of series, shunt, compound, permanent magnet, and separately excited motors • Describe the operation of series, shunt, compound, permanent magnet, and separately excited motors • Describe the applications of series, shunt, compound, permanent magnet, and separately excited motors • Describe how motor direction reversal is accomplished • Identify some advantages and disadvantages of DC motors
Specs
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of DC motors used?
What are DC motors commonly used for?
What are some of the advantages of a DC motor?
What are some of the disadvantages of a DC motor?
Sample Video Transcript
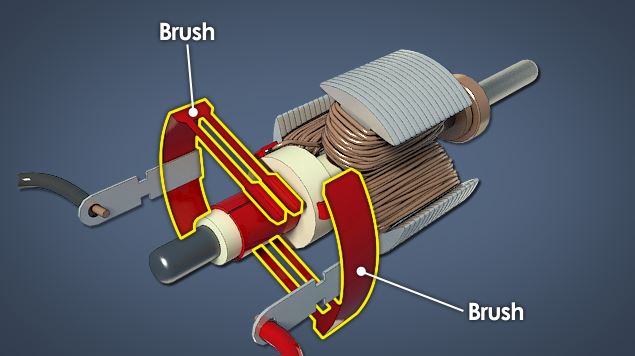
While there are important advantages of DC motors, including compact design and battery operation for portability, as well as a high degree of torque and speed control, DC motors have some inherent disadvantages that include relatively high initial cost and short operational lifespan for heavy-use industrial applications. High maintenance due to wear of brushes and commutators. Potential for sparks between contact surfaces, requiring operation outside of hazardous or explosive environments. And possible radio frequency or RF interference with nearby devices due to strong magnetic fields produced by the stator.