Electric Motor Basics
Electric motors are key components of many consumer products and industrial processes, from kitchen mixers to pump motors generating thousands of horsepower. This course describes the operation and common uses for AC motors, DC motors, servomotors, and linear motors.







Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.
Course Details
Learning Objectives
• Describe the purpose and operation of an alternating current induction motor
• Describe the purpose and operation of a direct current motor
• Describe the purpose and operation of a servomotor
• Describe the purpose and operation of a linear motor
Specs
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common types of industrial electric motors?
What are the main components of an AC induction motor
What are some advantages of DC motors?
What is a servomotor?
What are some applications of linear motors?
Sample Video Transcript
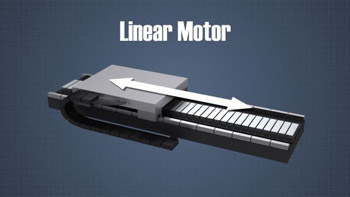
A linear motor is an electric induction motor that produces a linear force instead of a rotation. This is accomplished by unrolling the stator and rotor. The stator known as the platen in a linear motor, is a track of flat coils of copper or aluminum. The rotor takes the form of a moving carriage known as the forcer. When the current is switched on, the forcer glides past the platen supported and propelled by a magnetic field.