Photoswitches, Proximity Sensors, and Feedback Devices
Photoswitches, proximity sensors, and feedback devices are all used to detect objects or information. They are useful in industrial and manufacturing environments to sense product or personnel in the line of machinery or equipment. This module discusses the operation of the different types of each of these.







Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.
Course Details
Learning Objectives
• Describe the purpose of a photoswitch and its general operating principles
• Differentiate between the five basic types of photoswitches (retroreflective, thru-beam, polarized, diffuse, and convergent beam)
• Match the three basic types of proximity sensors (inductive, capacitive, and ultrasonic) with their principles of operation
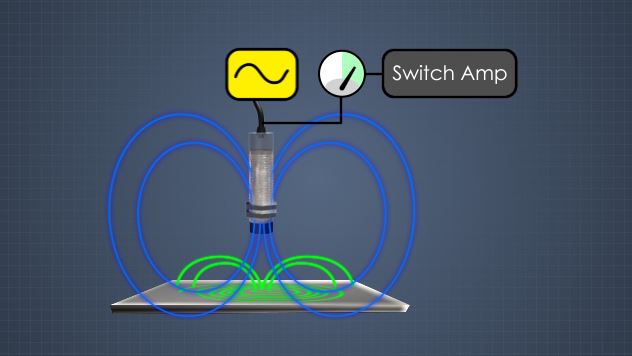
• Describe the purpose of a proximity sensor
• Explain the operation of three feedback devices (incremental encoders, absolute encoders, and Hall effect sensors)
• Describe the purpose of a feedback device
Specs
Frequently Asked Questions
What are photoswitches, proximity sensors, and feedback devices used for?
What is a photoswitch?
What are some common types of photoswitches?
What are proximity sensors?
What are some common types of proximity sensors?
What are feedback devices?
What are some common types of feedback devices?
Sample Video Transcript
Unlike the incremental encoder, the absolute encoder obtains position information. The absolute encoder has multiple rings etched on the disk. The first ring has one light segment and one dark segment, each successive ring has doubled the number of segments from the previous ring. The number of rings determines the number of bits of resolution of the encoder. This can be used to determine the number of steps that an encoder can detect. The output of the device is a binary number. As the disk turns, the binary number increases. Absolute encoders typically use a binary code called the gray code, in which only one bit changes as the sequence increases. The binary number or gray code number can be used to determine shaft position.