Power Boiler Fuel Supply Systems
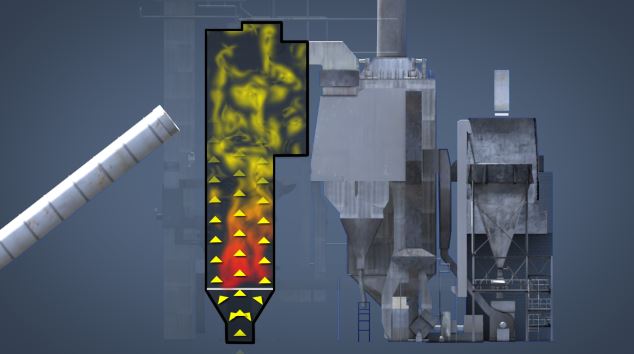
In order for a boiler to convert water to steam, a fuel source must release its energy in the form of combustion in the boiler furnace. Fuel systems play a critical role in the performance of a boiler. The most commonly used fuels in power boilers are natural gas, fuel oil, coal, and wood (biomass). Each of these fuels have different physical properties that require delivery systems that are unique to that fuel. Fuel systems should be properly operated and maintained to run efficiently.








Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.
Course Details
Learning Objectives
• Explain the purpose of a fuel source in a power boiler
• Describe the fuel considerations taken when designing a boiler
• Identify and describe the safety hazards and safe work practices associated with power boiler fuel systems
• Describe the primary function of power boiler fuel supply systems
• Differentiate between gaseous, liquid, and solid fuels
• Identify the most commonly used fuels in power boilers
• Identify and describe key equipment
• Describe the operation of natural gas, fuel oil, coal, and biomass power boiler fuel systems
Specs
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a fuel source in a power boiler?
What are the fuel considerations taken when designing a boiler?
What are some characteristics of gaseous fuels?
What are some characteristics of liquid fuels?
What are some characteristics of solid fuels?
Sample Video Transcript
The purpose of a power boiler is to create steam by applying heat energy to water. In order for a boiler to convert water to steam, a fuel source must release its energy in the form of combustion in the boiler furnace. A variety of fuels are available for use in boilers, each having different chemical properties. Each different fuel requires its own apparatus to handle, store, and deliver the fuel to the boiler. When designing a boiler, consideration is given to cost of a fuel, availability of a fuel, efficiency of a fuel, and burning characteristics of a fuel. Every fuel, whether it is in solid, liquid, or gaseous form, is explosive, and can prove hazardous if not used according to the recommended safety guidelines.