Recausticizing Fundamentals
Includes an overview of the kraft pulping process and recausticizing system, and describes how recaust converts the chemicals in spent cooking liquor back to their original form. It describes the major equipment and processes, including the slaking, causticizing, and calcining reactions.








Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.
Course Details
Learning Objectives
• Describe the kraft pulping process
• Describe the role of chemical recovery and recausticizing systems in the kraft pulping process
• Identify flows and major equipment in the recausticizing system
• Describe the chemical reactions that occur during pulping and in the recausticizing system
• Identify the components of the strong black liquor sent to the recovery boiler
Specs
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the source of green liquor?
What is slaking?
What is causticizing?
What is calcining?
What are grits?
Sample Video Transcript
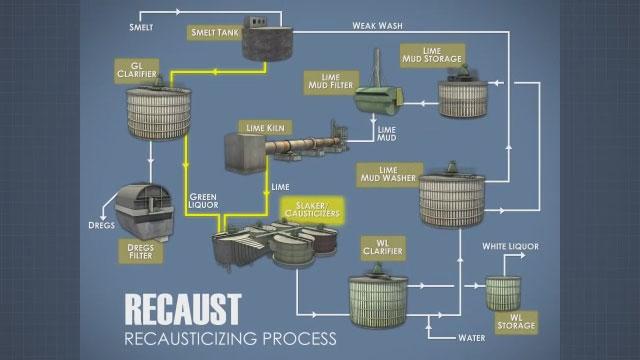
Now that we have discussed the role of the recausticizing system in the kraft pulping process, we will detail the system equipment and operations, starting with the green liquor clarifier and ending at the lime kiln. The green liquor clarifier purifies the green liquor from the smelt dissolving tank before it enters the recaust system. A sedimentation clarifier is typically used. A sedimentation clarifier is a tank or basin that provides the time necessary for suspended solids in a liquid to settle out. The small solid particles that are suspended in the green liquor are called dregs. Once the dregs have settled out, they can be removed from the bottom of the clarifier by a rake mechanism and center sludge outlet. After the clarifier, the dregs are washed and filtered on the dregs filter, which recovers most of the valuable cooking chemicals they contain. Finally, they are discharged from the system as waste.